Climate Variability and Health
Addressing the health impacts of climate change requires practical, science-based strategies that protect public health while maintaining economic stability. Although there remains ongoing discussion about the extent of human influence on climate patterns, it is prudent to prepare for environmental changes that may affect air and water quality, increase the prevalence of vector-borne diseases, and impact food and water security. Strengthening community resilience through investments in reliable infrastructure, support for local agriculture, and promotion of energy efficiency can enhance public health outcomes without imposing excessive regulatory burdens on industry or hindering economic growth. Responsible environmental stewardship—anchored in innovation, individual responsibility, and respect for local decision-making—offers a balanced approach to mitigating health risks associated with climate variability.
How Climate Affects Health
Scientific understanding of climate variability continues to evolve, but its effects on human health are increasingly evident. Shifts in climate can contribute to droughts and extreme flooding, which may compromise drinking water quality, food safety, and air purity, thereby elevating the risk of illness and injury. Periods of extreme heat or cold can lead to serious health issues, including heat stroke or hypothermia, and may worsen chronic conditions such as asthma, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Additionally, changing temperatures and precipitation patterns expand the habitat for disease-carrying vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks, increasing the risk of illnesses like West Nile Virus and Lyme disease. These infectious diseases can spread rapidly when environmental conditions become more favorable for vector breeding, highlighting the importance of preparedness and adaptation.
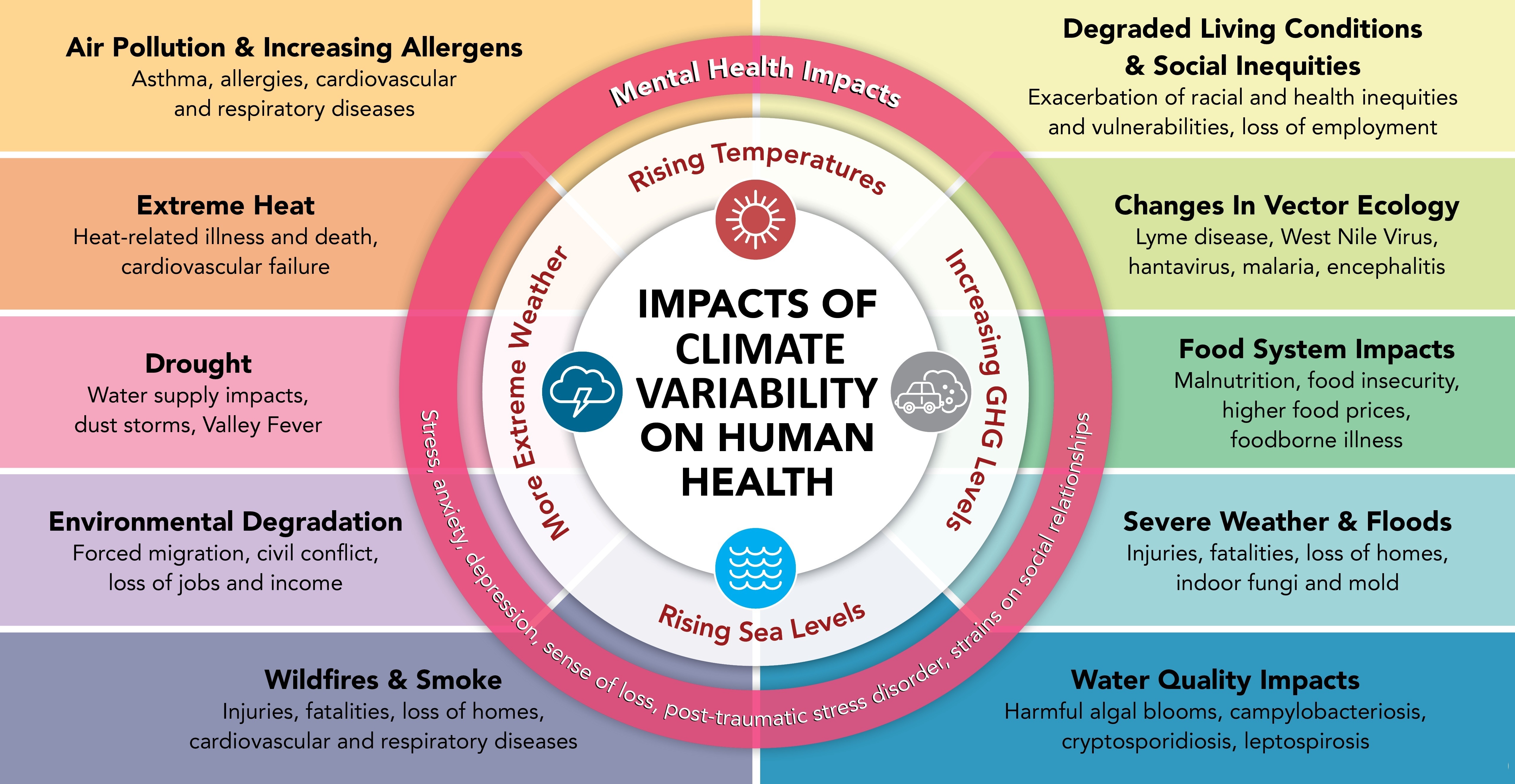
Responding to Climate Variability
New York State works to address climate variation and protect New Yorkers:
- The Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (Climate Act), which was passed in July of 2019, is among the most ambitious climate laws in the nation. The Climate Act aims to reduce greenhouse gases from 1990 levels by 40% by 2030 and at least 85% by 2050 by increasing renewable energy use and ensuring all communities equitably benefit in the clean energy transition.
- New York State’s Extreme Heat Action Plan identifies and supports initiatives to keep residents safe and prepare communities for rising temperatures.
- New York State's emergency preparedness programs protect New Yorkers, their property, and our economic well-being from emergencies and disasters.
What You Can Do
Follow these steps to help protect yourself and your family:
- Be informed and prepared: Learn more about emergency preparedness, extreme storms and flooding, outdoor air quality, harmful blue-green algae blooms, extreme heat and extreme cold weather, and tick-borne and mosquito-borne diseases.
- Find out about how climate variation affects your community: Use our Air Quality Index, Heat Vulnerability Index Maps, and Environmental Public Health Tracker.
- Use tools and resources that can help you cope with changes in temperature such as the NYS Cooling Center Finder and Cooling Assistance Benefit Program.


